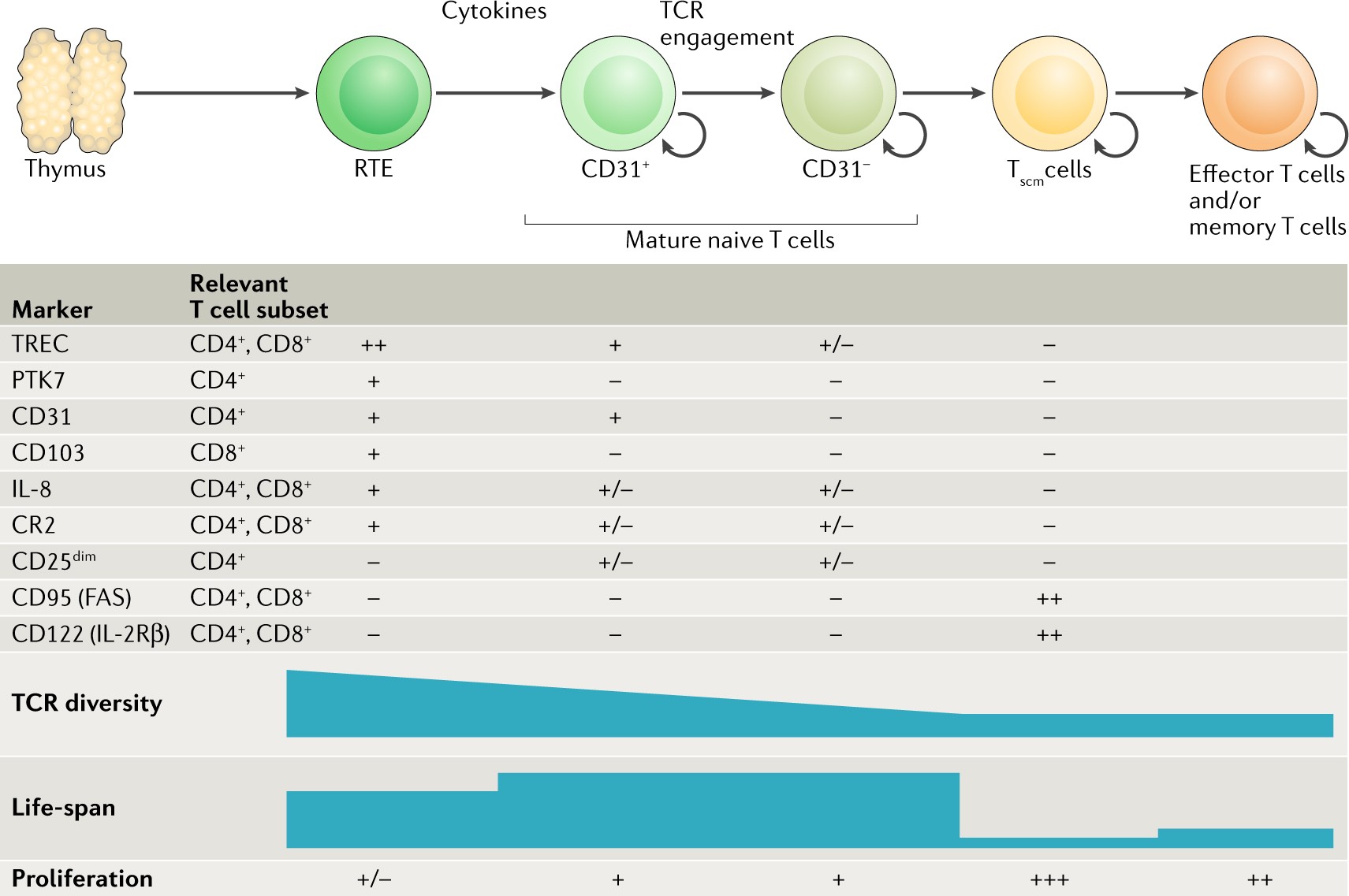
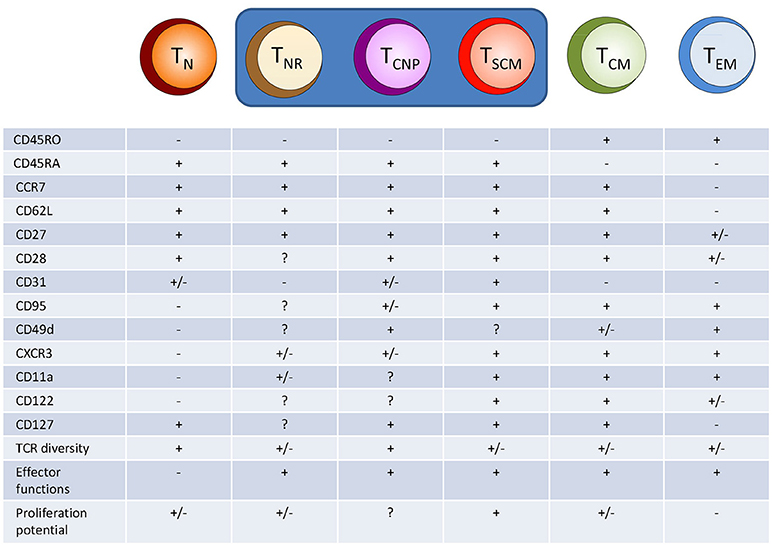
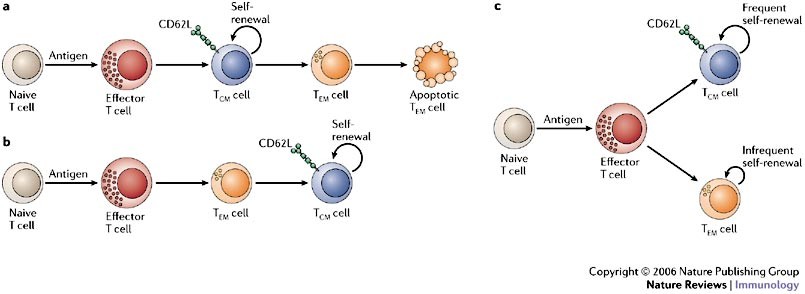
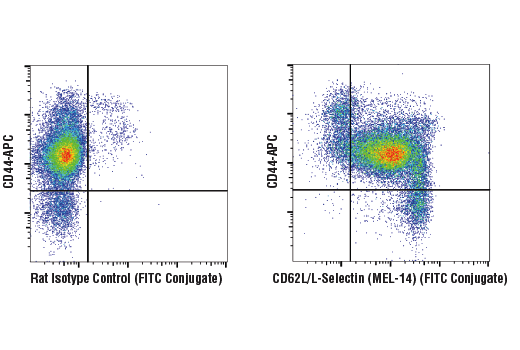
The who's who of T‐cell differentiation: Human memory T‐cell subsets - Mahnke - 2013 - European Journal of Immunology - Wiley Online Library
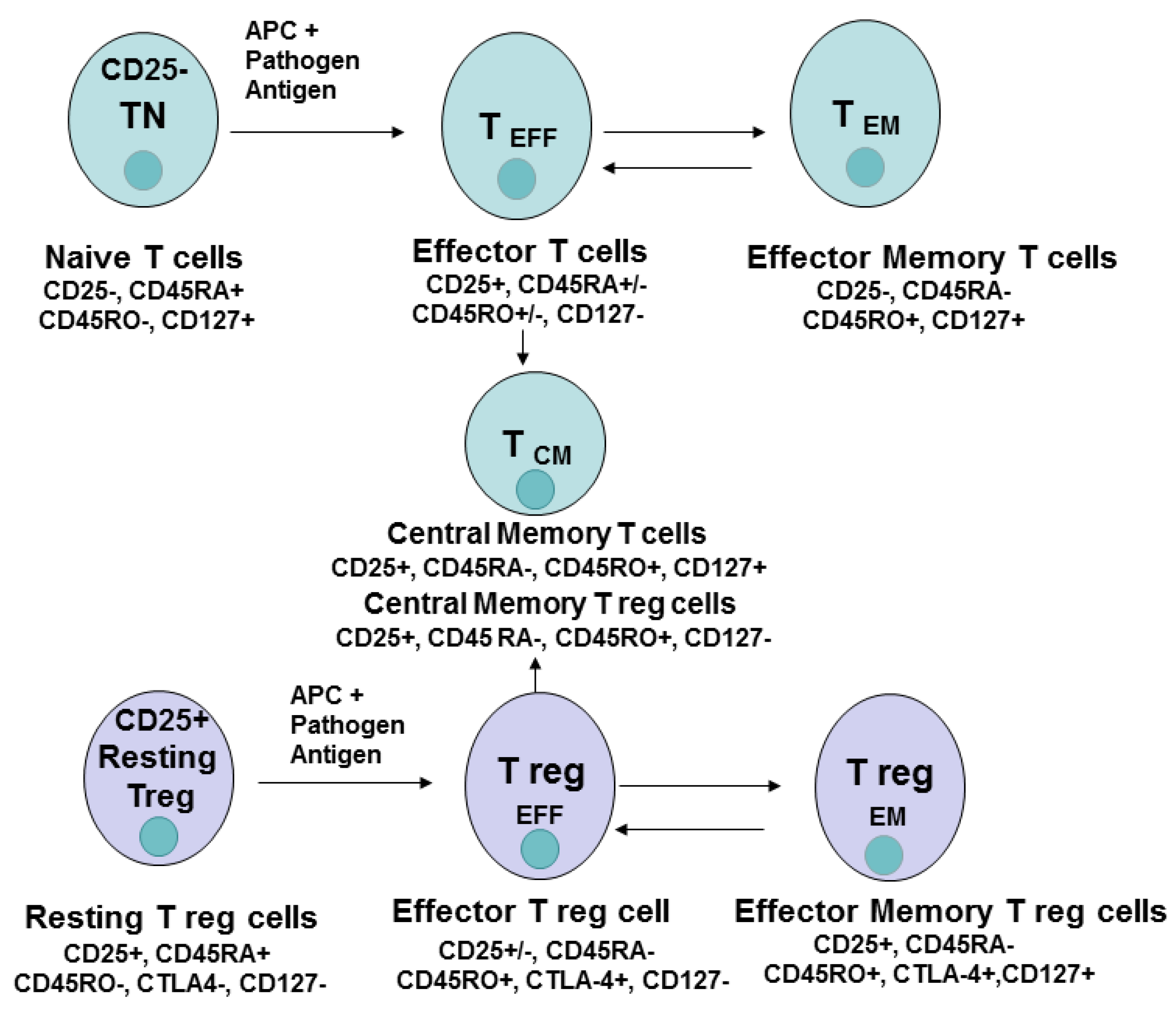
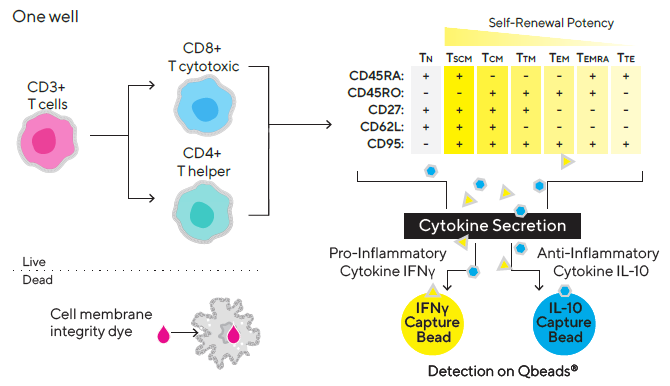
Cancers | Free Full-Text | Different Subsets of T Cells, Memory, Effector Functions, and CAR-T Immunotherapy
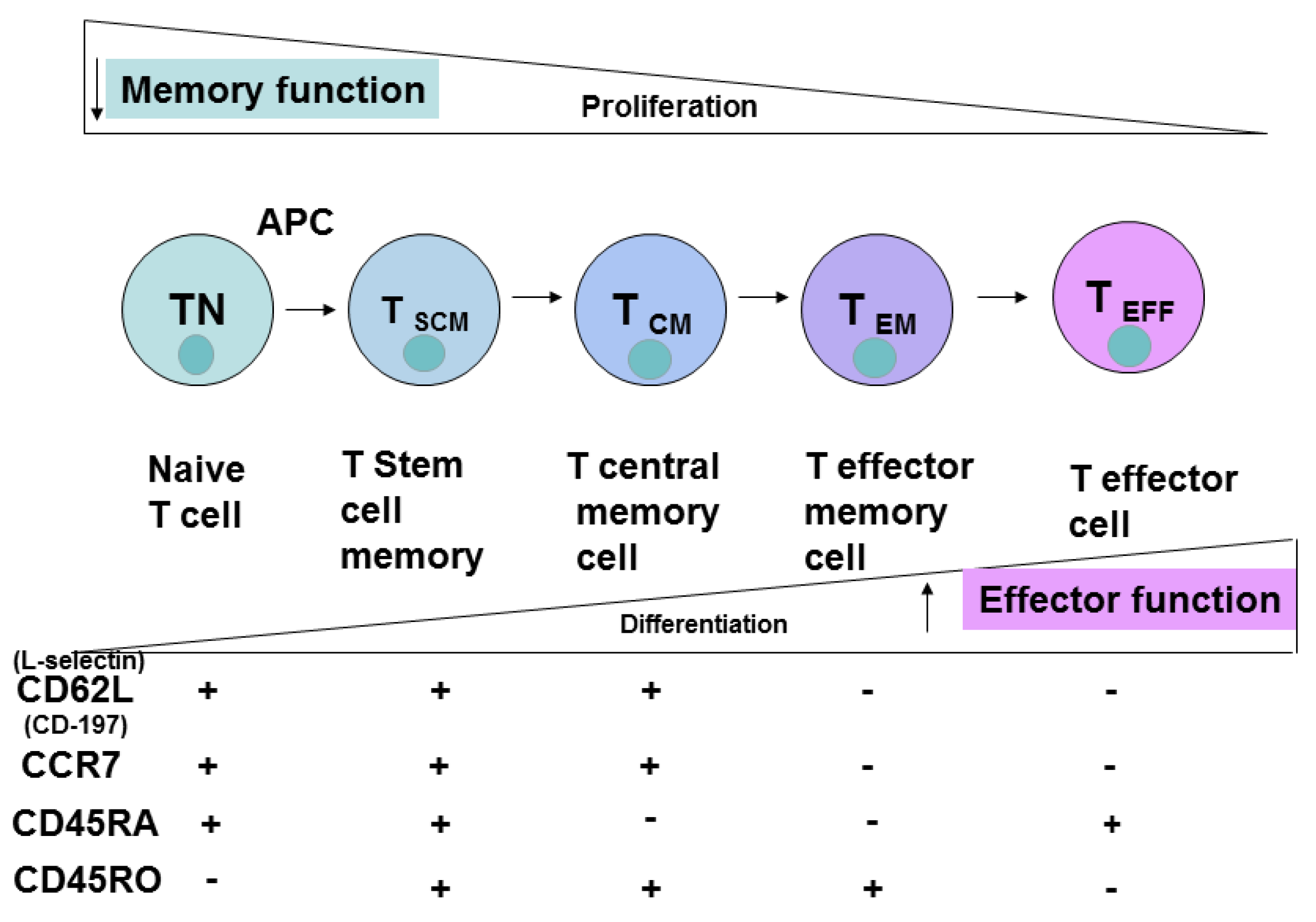
Cancers | Free Full-Text | Different Subsets of T Cells, Memory, Effector Functions, and CAR-T Immunotherapy

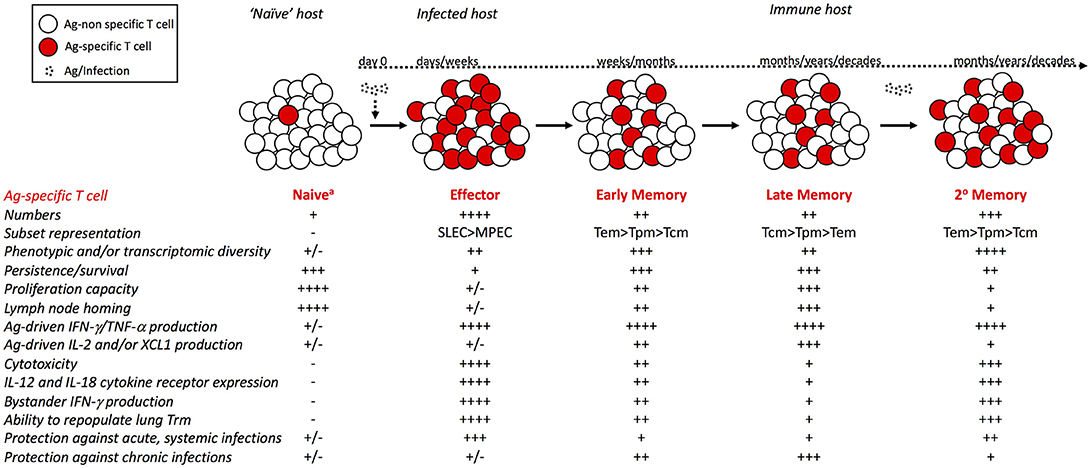
The human CD8 T stem cell-like memory phenotype appears in the acute phase in Yellow Fever virus vaccination | bioRxiv

IJMS | Free Full-Text | CD8+ T Cell Phenotype and Function in Childhood and Adult-Onset Connective Tissue Disease
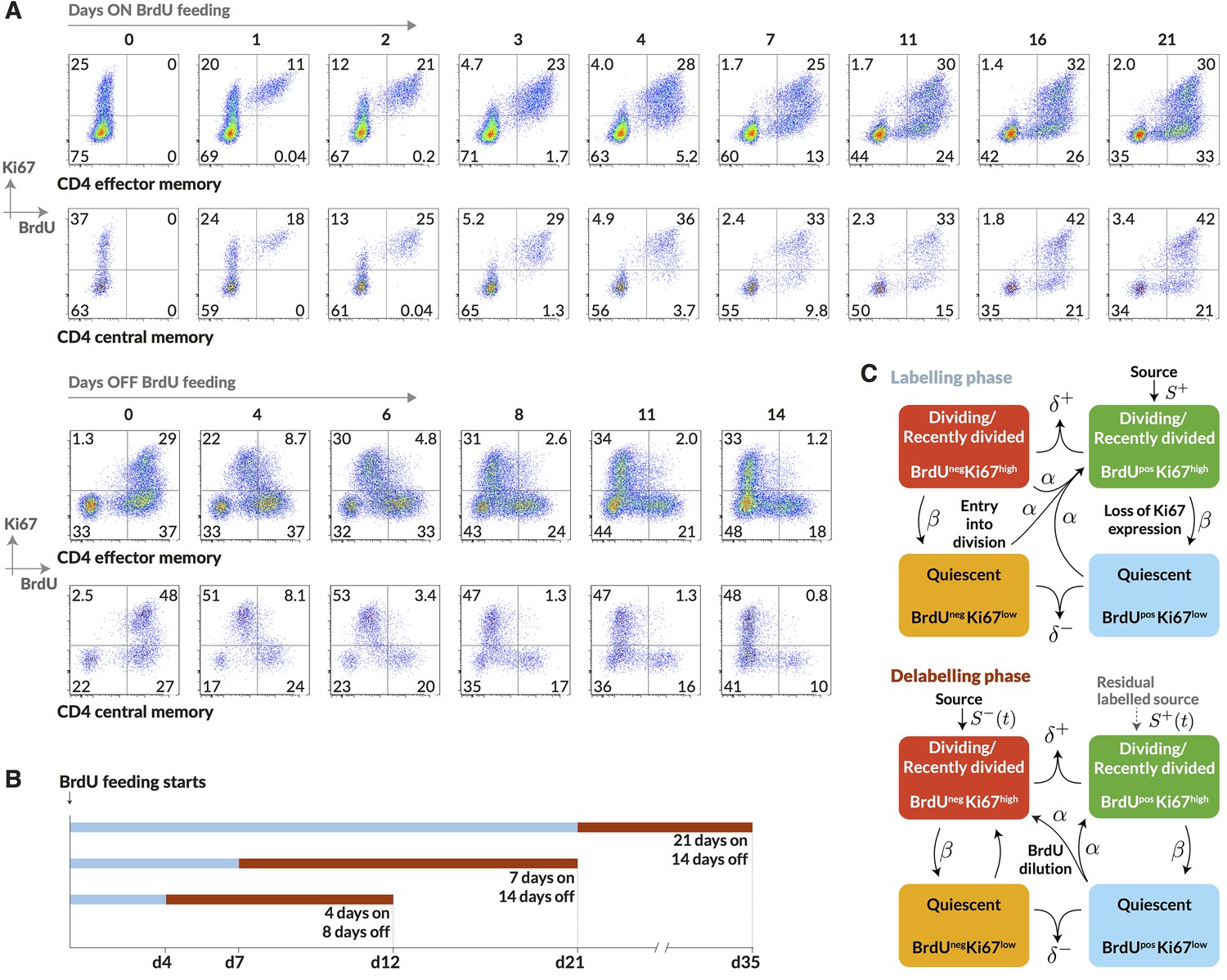
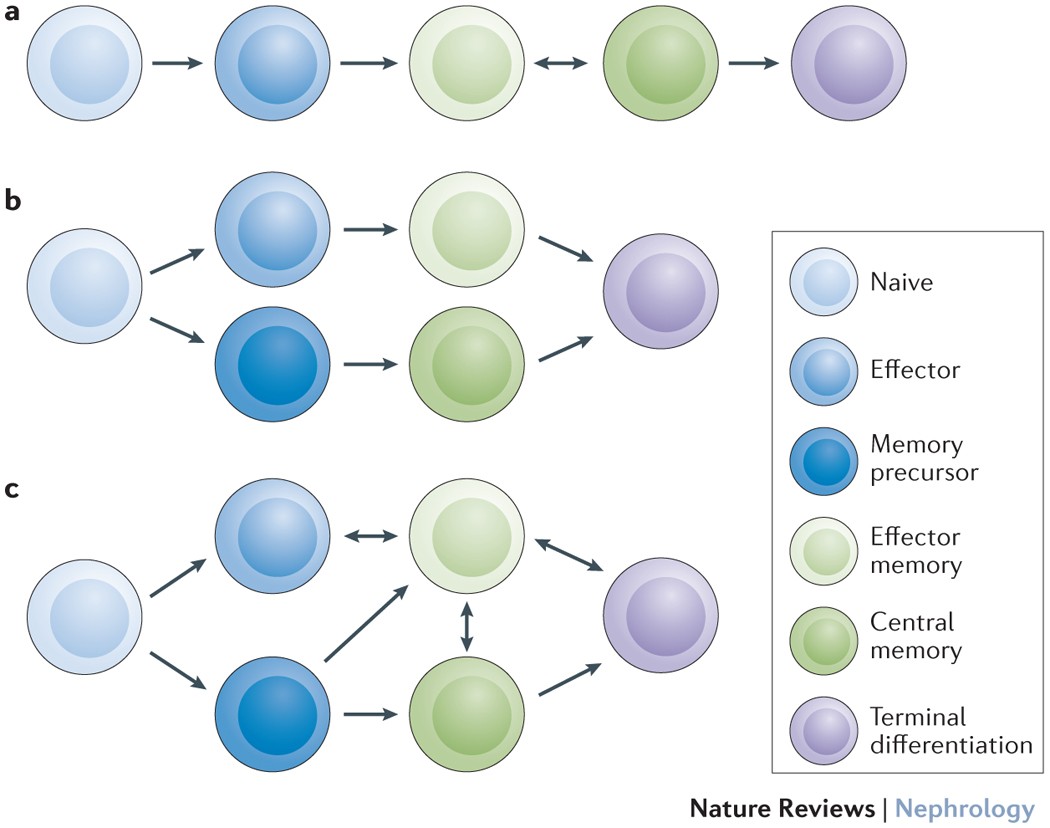
Memory CD4 T cell subsets are kinetically heterogeneous and replenished from naive T cells at high levels | eLife